Monitoring Compressed Air with LoRaWAN Solution
Introduction
The system tracks crucial data from compressor, dryer, and filter units situated at three distinct locations within the facility. By utilizing LoRaWAN technology, the solution enables real-time, centralized monitoring, analysis, and early detection of maintenance needs, significantly improving overall system efficiency
Common Challenges in Factory Monitoring
-
Geographical Dispersion and Distance: Components like pipelines and monitoring points (compressors, dryers, filters) are spread across different zones and are distant from each other, making wired solutions impractical.
-
High Cabling Costs and Complexity: Establishing physical cable connections across vast distances for data transmission is expensive, complex, and time-consuming.
-
Signal Obstruction: Difficult industrial settings, such as those that are enclosed or dense with metal, often disrupt traditional wireless communication signals.
-
Need for Centralized Management: Monitoring systems spread across large areas often lack a unified, real-time platform for centralized data analysis and alarm management.
Application Concept
-
Flow and Consumption Measurement: SUTO flow meters are installed to measure key consumption metrics including flow rate, temperature, pressure, velocity, dew point, and power consumption.
-
Data Acquisition (WISE-2200): The Advantech WISE-2200 module is connected to the SUTO flow meters and collects data via Modbus/RTU.
-
Centralized Gateway (WISE-6610 V2): The gateway receives the wireless LoRaWAN data , aggregates it centrally, and can handle data from up to 500 different points.
-
Edge Processing and Protocols: The gateway features a built-in Node-RED environment for executing logic and algorithms at the edge. It also supports data transmission to software platforms using protocols like WebService, MQTT, and ModbusTCP.
-
Monitoring and Analysis (S4M Software): All measurements are monitored in real time using analysis features like graphs, trends, and alarm management
System Architecture Overview
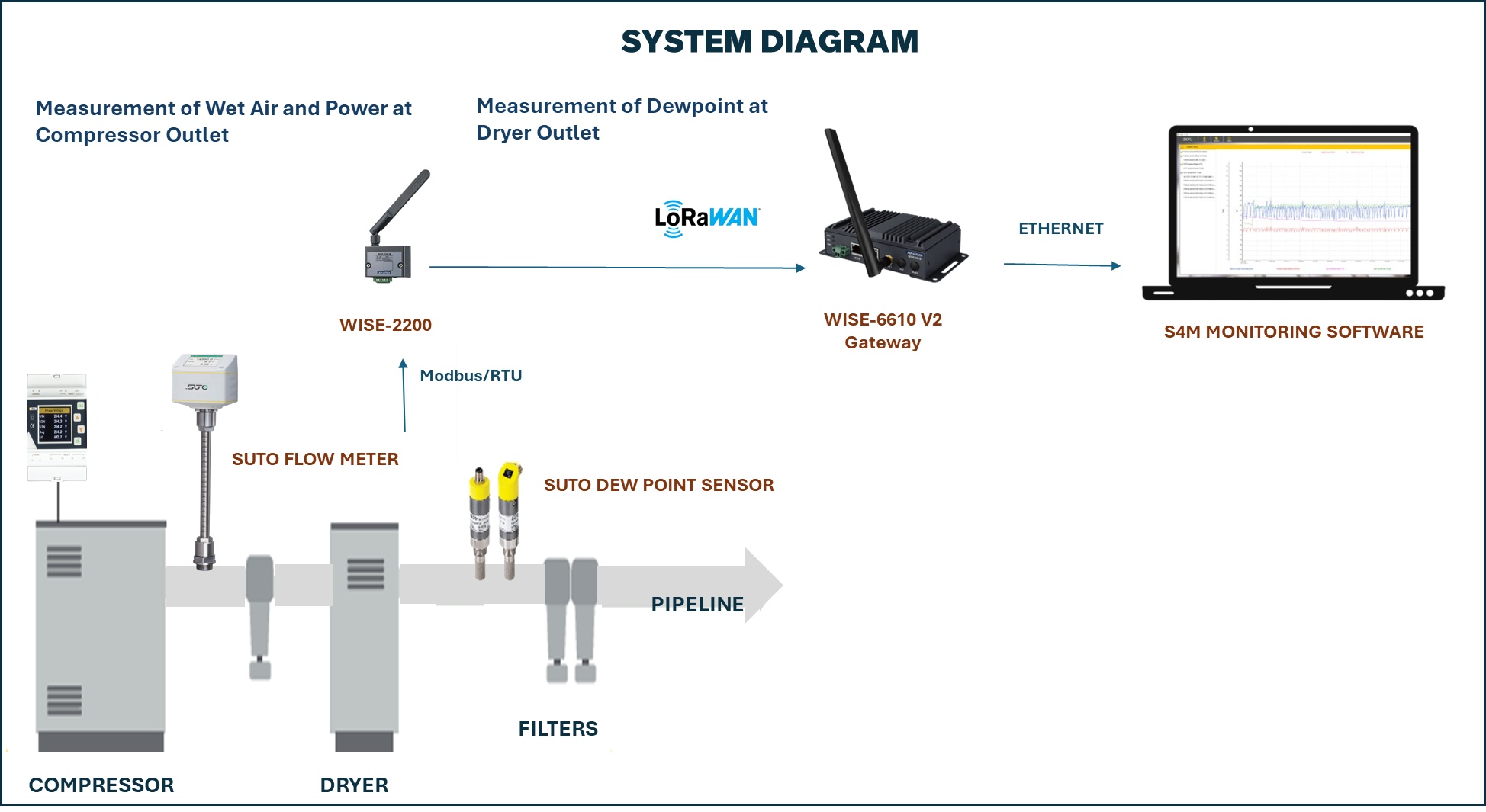
This compressed air monitoring system uses a distributed sensor network, beginning with measurement points like compressor units, filters, and a dryer, which are equipped with SUTO Flow Meters and Dew Point Sensors to capture metrics such as wet air, power, and dew point. The data is collected by an edge node via Modbus RTU through the WISE-2200, then transmitted wirelessly over the long-range LoRaWAN protocol to the central WISE-6610 V2 gateway. The gateway then relays the collected data using Ethernet to a central monitoring software (S4M), which provides real-time analysis, graphing, and alarm management functions.
System Diagram
Key Benefits
-
Significant Cost Savings: Wireless LoRaWAN communication eliminates expensive cabling, resulting in substantial cost reductions.
-
Enhanced Coverage and Reliability: LoRaWAN offers high coverage with low interference. The system maintains a stable connection, communicating wirelessly over 300–400 meters even in metal-dense environments.
-
Centralized Real-Time Management: Data from large, spread-out areas is monitored in real time from a single platform, allowing for advanced detection of maintenance needs.
-
Scalability and Flexibility: The flexible, distributed architecture supports multi-sensor systems and is scalable, with the WISE-6610 supporting data from up to 500 different points.
-
Easy Deployment: Components feature a compact, industrial-grade design for easy, plug-and-play installation suitable for diverse environments
Conclusion
The successful implementation of this Advantech and SUTO system leveraging LoRaWAN demonstrates a highly effective model for Industrial IoT applications. By overcoming the challenges of distance and cabling in large-scale industrial settings, the system provides essential real-time data for optimizing compressed air efficiency and streamlining maintenance operations. This approach validates LoRaWAN as a strategic, cost-effective, and robust communication technology for comprehensive industrial monitoring.

